What is Immune Cell Banking?
The human body’s immune system is an amazing system that allows the body to repair itself & fight off disease, bacteria & infection through speciazlied types cells called immune cells. It is the power of our immune cells that doctors want to harness to treat complex diseases, such as cancer, like a form of personalized medicine. HealthBanks is proud to be the only dual biobank in the US that collects, processes & stores immune cells from adult whole blood & stem cells from newborn umbilical cord blood.
The purpose of banking your healthy immune cells today is to have them safely preserved so they can be used in cell-based therapies of the future. Preserving the immune cells while they are young & healthy before they are needed is key. Equipped with the latest in automated processing & cryogenic storage technology, we preserve your family’s cells safely in our state-of-the-art cryogenic storage tanks, essentially freezing them in time. Founded by professionals in the stem cell banking industry, we have developed a reliable cell banking system that helps families preserve today’s healthy cells for the developing cell & gene therapies of tomorrow.
What is the process for Immune Cell Banking?
The process for immune cell preservation is the same as giving blood. The process begins by visiting a blood collection center where a 150-200mL blood draw will be collected. Your blood will then be sent to our certified processing facility within 24 hours to isolate peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) which contains all the immune cells. After the processing is complete, we will store your cells at -196°C for long-term storage. Cells can be preserved in this state for very long periods of time without any significant change in cell viability.
What can you use preserved immune cells for?
Immunotherapy is an emerging type of treatment that uses a patient’s own immune cells to fight life-threatening diseases, such as cancer. This is important because the average person’s likelihood of developing cancer in their life is about 33% which increases as we age. As of 2023, there are now at least 6 FDA approved cell-based immunotherapies for cancer treatment with many more currently being researched every day. “Immunotherapy cancer treatments are now part of modern medicine and represent a huge advance in the way cancer can be treated.” – Dr. Renier J. Brentjens from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York saying immunotherapy cancer treatment is “the equivalent of giving patients a living drug.” This is a great explanation since the treatment uses the patient’s own healthy, living cells.
One of the leading immunotherapies is called CAR-T cell therapy. Before the patient becomes ill, healthy T cells are collected from their blood & stored. The preserved T cells can be modified with specific receptors to target cancer cells called Chimeric Antigen Receptors (CAR). These modified CAR-T cells are injected back into the patient which target cancer cells. The modified CAR-T cells attach to specific antigens on the tumors & kill the cancer cell.
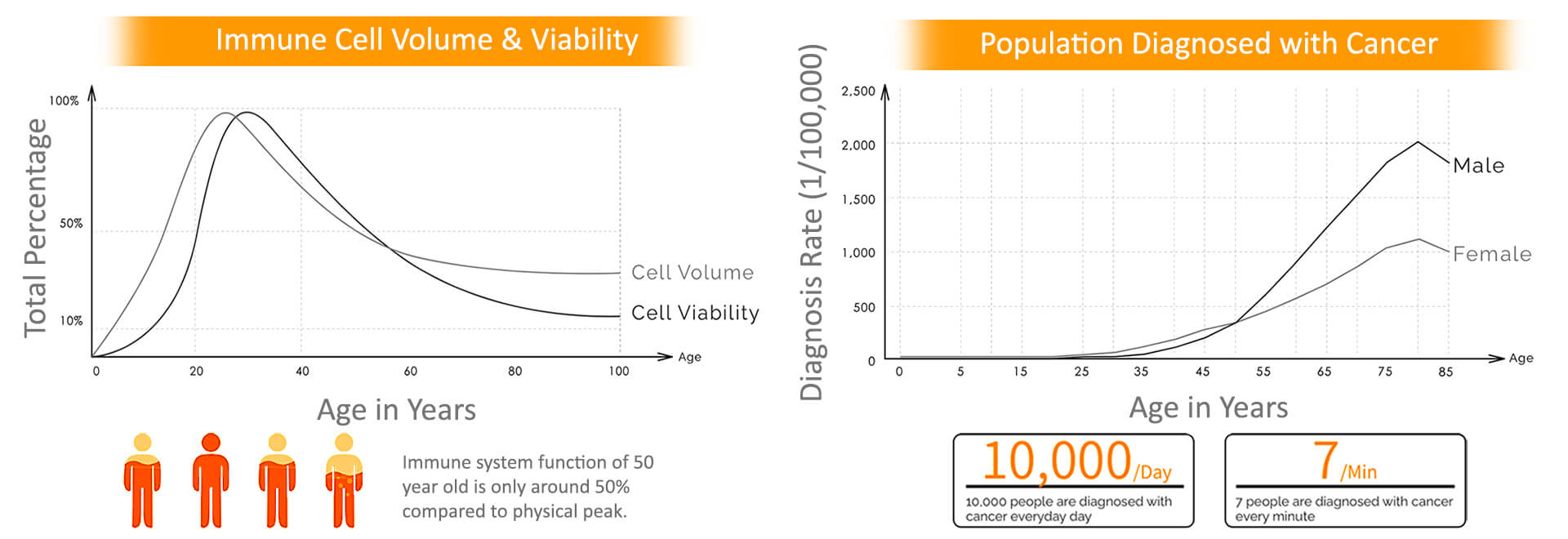
Aging
The body’s immune system decays over age. The effects of aging on the immune system manifest at multiple levels including reduced production of B & T cells in bone marrow & thymus with diminished function of mature lymphocytes in secondary lymphoid tissues. As a result, elderly individuals do not respond to immune challenge as robustly as the young.
Cancer Treatments
The immune system is one of the most vulnerable targets during cancer treatment. Compounded by the use of chemotherapy & radiotherapy, a patient’s immune system is severely damaged with typical cancer treatments.
T Cell Count
In many cases of advanced cancer, cancer cells will enter circulation & interfere with the body’s natural production of immune cells. As a result, many cancer patients fail to obtain enough healthy T cells to allow the production of enough effector cells for treatment.